ପ୍ରସବ
ପ୍ରସବ (ଅନ୍ୟ ନାମ ଲେବର ବା ଡେଲିଭରି) ନାମ ଦିଆଯାଏ ଯେତେବେଳେ ଗର୍ଭାବସ୍ଥାର ଅନ୍ତରେ ଏକ ବା ଏକାଧିକ ଶିଶୁ ମହିଳାର ଜରାୟୁରୁ ବାହାରକୁ ଆସନ୍ତି ।[୧] ସାରା ପୃଥିବୀରେ ସନ ୨୦୧୫ରେ ପ୍ରାୟ ୧୩୫ ନିୟୁତ ଶିଶୁ ଜନ୍ମ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।[୨] ଏଥି ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ପ୍ରାୟ ୧୫ ନିୟୁତ ଅବଧିପୂର୍ବ ପ୍ରସବ (୩୭ ସପ୍ତାହ ପୂର୍ବରୁ) ଥିଲା,[୩] ଓ ୩ରୁ ୧୨% ପ୍ରସବ ଅବଧିପର ପ୍ରସବ (୪୨ ସପ୍ତାହ ପରେ) ଥିଲା ।[୪] ବିକଶିତ ଦେଶମାନଙ୍କରେ ଅଧିକାଂଶ ପ୍ରସବ ଡାକ୍ତରଖାନାରେ ହୁଏ,[୫][୬] ଓ ବିକାଶଶୀଳ ଦେଶମାନଙ୍କରେ ଅଧିକାଂଶ ପ୍ରସବ ଧାଇମାନଙ୍କ ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ହୁଏ ।[୭]
| ପ୍ରସବ | |
|---|---|
| ଇଂରାଜୀ ପ୍ରତିଶବ୍ଦ- partus, parturition, birth | |
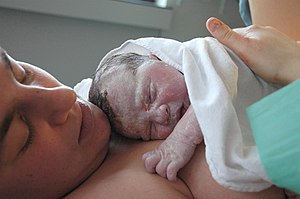 ନବଜାତ ଶିଶୁ ଓ ମାତା | |
| ବିଭାଗ | Obstetrics, midwifery |
ଅଧିକାଂଶ ଡେଲିଭରି ଯୋନୀପଥ ପ୍ରସବ (vaginal delivery) ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ହୁଏ । [୮] ଏହି ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ତୋନୋଟି ସୋପାନ ଥାଏ: ୧. ଜରାୟୂଗ୍ରୀବା ସଙ୍କୋଚନ (shortening) ଓ ଜରାୟୁ ମୁଖ ପ୍ରସାରଣ (opening of the cervix|), ୨. ନିମ୍ନଗମନ ଓ ପ୍ରସବ ୩. ପ୍ରସବ ଫୁଲର (placenta) ବହିଷ୍କାର ।[୯] ପ୍ରଥମ ସୋପାନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ୧୨ରୁ ୧୯ ଘଣ୍ଟା ଲାଗେ, ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ସୋପାନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ୨୦ ମିନିଟରୁ ୨ ଘଣ୍ଟା ଲାଗେ ଓ ତୃତୀୟ ସୋପାନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ୫ରୁ ୩୦ ମିନିଟ ଲାଗେ ।[୧୦] ପ୍ରଥମ ସୋପାନରେ ଉଦର ଶୂଳ (crampy abdominal pains) ବା କଟି ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇ ପ୍ରାୟ ଅଧ ମିନିଟ ରହେ ଓ ପ୍ରତି ୧୦ରୁ ୩୦ ମିନିଟରେ ପୁନର୍ବାର ହୁଏ ।[୯] ଉଦର ଶୂଳ ସମୟକ୍ରମେ ଶକ୍ତ ହୁଏ ଓ ଅଳ୍ପ ସମୟ ଅନ୍ତରରେ ବାରମ୍ବାର ହୁଏ ।[୧୦] ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ସୋପାନରେ ଜରାୟୁ ସଙ୍କୋଚନଦ୍ୱାରା ଶିଶୁ ଠେଲିହୋଇ ବାହାରକୁ ଆସେ ।[୧୦] ତୃତୀୟ ସୋପାନରେ ବିଳମ୍ବିତ ନାହି କଟା ସୁପାରିସ କରାଯାଏ । [୧୧] ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଉପଶମ ନିମନ୍ତେ ରିଲାକ୍ସେସନ ପଦ୍ଧତି, ଓପିଅଏଡ (opioids) ଓ ସ୍ପାଇନାଲ ବ୍ଲକ (spinal block) ଉପାୟମାନ ଅବଲମ୍ବନ କରାଯାଏ ।[୧୦]
ଅଧିକାଂଶ ପ୍ରସବରେ ଶିଶୁର ମୁଣ୍ଡ ପ୍ରଥମେ ଜନ୍ମ ହୁଏ; ୪% ଶିଶୁର ପାଦ ବା ନିତମ୍ବ (ପିଚା) ପ୍ରଥମେ ଜନ୍ମ ହୁଏ ।[୧୦][୧୨] ପ୍ରସବ ସମୟରେ ଜଣେ ମହିଳା ଇଚ୍ଛାନୁସାରେ ଚଳପ୍ରଚଳ ହୋଇପାରିବ ଓ ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଖାଇପାରିବ; ମୁଣ୍ଡ ବାହାରକୁ ଆସିବା ବେଳେ ବା ପ୍ରଥମ ସୋପାନରେ ଶିଶୁକୁ ଜରାୟୁରୁ ଠେଲି ବାହାର କରିବାକୁ ଅନୁମତି ଦିଆଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ଓ ଏନିମା ଦେବାକୁ ସୁପାରିସ କରାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।[୧୩] ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଏପିସିଓଟୋମି (episiotomy) ବା ଯୋନୀପଥ ମୁଖକୁ ଅପରେଶନ କରି ପ୍ରସାରିତ କରାଯାଉଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତାହା କରିବାକୁ ଉପଦେଶ ଦିଆଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।[୧୦] ସନ ୨୦୧୨ରେ ପ୍ରାୟ ୨୩ ନିୟୁତ ସିଜରିଆନ ସେକସନ (Caesarean section) ଅପରେଶନ କରାଯାଇଥିଲା ।[୧୪] ଯାଆଁଳା ଛୁଆ ଥିଲେ, ଫିଟାଲ ଡିସ୍ଟ୍ରେସ (signs of distress in the baby) ହେଉଥିଲେ ବା ବ୍ରିଚ ପୋଜିସନରେ ଶିଶୁ ଥିଲେ ସିଜରିଆନ ସେକସନ କରି ଶିଶୁକୁ ବାହାର କରାଯାଏ ।[୧୦] ଏହି ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ କ୍ଷତ ଶୁଖିବାକୁ ଅଧିକ ସମୟ ଲାଗେ । [୧୦]
ପ୍ରତିବର୍ଷ ଗର୍ଭାବସ୍ଥା ଓ ପ୍ରସବ ଜଟିଳତା ଯୋଗୁ ୫୦୦,୦୦୦ ମାତୃ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ (maternal deaths) ହୁଏ, ୭ ନିୟୁତ ମହିଳାଙ୍କର ସାଂଘାତିକ ଦୀର୍ଘକାଳୀନ ସମସ୍ୟା ରହେ ଓ ୫୦ ନିୟୁତ ମହିଳାଙ୍କର ପ୍ରସବପର ସ୍ୱାସ୍ଥ୍ୟ ଫଳାଫଳ ବିଯୁକ୍ତାତ୍ମକ ରହେ ।[୧୫] ବିକାଶଶୀଳ ଦେଶମାନଙ୍କରେ ଏହି ସମସ୍ୟା ଅଧିକ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।[୧୫] ବାଧାପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ପ୍ରସବ (obstructed labour), ପ୍ରସବପର ରକ୍ତସ୍ରାବ (postpartum bleeding), ଏକ୍ଲାମ୍ପସିଆ (eclampsia) ଓ ପ୍ରସବପର ସଂକ୍ରମଣ (postpartum infection) ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧଷ୍ଟ ଜଟିଳ ସମସ୍ୟା ଜାତ ହୋଇପାରେ ।[୧୫] ପ୍ରସବ ସମୟରେ ଶିଶୁର ଅମ୍ଳଜାନ ଅଭାବ ହୋଇପାରେ ଯାହାକୁ ବାର୍ଥ ଆସଫିକ୍ସିଆ (birth asphyxia) କୁହାଯାଏ ।[୧୬]
ଆଧାର
ସମ୍ପାଦନା- ↑ Martin, Elizabeth. Concise Colour Medical Dictionary (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Oxford University Press. p. 375. ISBN 9780199687992.
- ↑ "The World Factbook". www.cia.gov. July 11, 2016. Archived from the original on 16 November 2016. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
- ↑ "Preterm birth Fact sheet N°363". WHO. November 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
- ↑ Buck, Germaine M.; Platt, Robert W. (2011). Reproductive and perinatal epidemiology. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 163. ISBN 9780199857746.
- ↑ Co-Operation, Organisation for Economic; Development (2009). Doing better for children. Paris: OECD. p. 105. ISBN 9789264059344.
- ↑ Olsen, O; Clausen, JA (12 September 2012). "Planned hospital birth versus planned home birth". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews (9): CD000352. PMID 22972043.
- ↑ Fossard, Esta de; Bailey, Michael (2016). Communication for Behavior Change: Volume lll: Using Entertainment–Education for Distance Education. SAGE Publications India. ISBN 9789351507581. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ Memon, HU; Handa, VL (May 2013). "Vaginal childbirth and pelvic floor disorders". Women's health (London, England). 9 (3): 265–77, quiz 276-7. PMID 23638782.
- ↑ ୯.୦ ୯.୧ "Birth". The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia (6 ed.). Columbia University Press. 2016. Retrieved 2016-07-30 from Encyclopedia.com.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ↑ ୧୦.୦ ୧୦.୧ ୧୦.୨ ୧୦.୩ ୧୦.୪ ୧୦.୫ ୧୦.୬ ୧୦.୭ "Pregnancy Labor and Birth". Women's Health. September 27, 2010. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ McDonald, SJ; Middleton, P; Dowswell, T; Morris, PS (11 July 2013). "Effect of timing of umbilical cord clamping of term infants on maternal and neonatal outcomes". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews (7): CD004074. PMID 23843134.
- ↑ Hofmeyr, GJ; Hannah, M; Lawrie, TA (21 July 2015). "Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews (7): CD000166. PMID 26196961.
- ↑ Childbirth: Labour, Delivery and Immediate Postpartum Care (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). World Health Organization. 2015. p. Chapter D. ISBN 978-92-4-154935-6. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ↑ Molina, G; Weiser, TG; Lipsitz, SR; Esquivel, MM; Uribe-Leitz, T; Azad, T; Shah, N; Semrau, K; Berry, WR; Gawande, AA; Haynes, AB (1 December 2015). "Relationship Between Cesarean Delivery Rate and Maternal and Neonatal Mortality". JAMA. 314 (21): 2263–70. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.15553. PMID 26624825.
- ↑ ୧୫.୦ ୧୫.୧ ୧୫.୨ Education material for teachers of midwifery : midwifery education modules (PDF) (2nd ed.). Geneva [Switzerland]: World Health Organisation. 2008. p. 3. ISBN 978-92-4-154666-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-02-21. Retrieved 2016-08-09.
- ↑ Martin, Richard J.; Fanaroff, Avroy A.; Walsh, Michele C. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine: Diseases of the Fetus and Infant (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 116. ISBN 9780323295376.