ବାଇକାଲୁଟାମାଇଡ
ବାଇକାଲୁଟାମାଇଡ (ଇଂରାଜୀ ଭାଷାରେ Bicalutamide, ବିକ୍ରୟ ନାମ କାସୋଡେକ୍ସ/ Casodex) ଏକ ଆଣ୍ଡ୍ରୋଜେନ ବିରୋଧୀ (antiandrogen) ଔଷଧ ଯାହା ପ୍ରୋସ୍ଟେଟ କର୍କଟ ରୋଗର ଚିକିତ୍ସା ନିମନ୍ତେ ଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧୧] ମେଟାସ୍ଟାସିସ (metastatic) ହୋଇଥିବା ପ୍ରୋସ୍ଟେଟ କର୍କଟ ରୋଗରେ ବା ଓର୍କିଡେକ୍ଟୋମି (surgical removal of the testicles) କରାଯାଇଥିଲେ ଏହା ଗୋନାଡୋଟ୍ରପିନ-ରିଲିଜିଙ୍ଗ ହରମୋନ ଆନାଲଗ (gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogue) ସାଥିରେ ଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧୨][୧୧][୧୩] ମହିଳାଙ୍କର ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ବାଳ ବୃଦ୍ଧି (excessive hair growth) ହୋଇଥିଲେ ବାଇକାଲୁଟାମାଇଡ ଦିଆଯାଏ,[୧୪] ଟ୍ରାନ୍ସଜେଣ୍ଡର ମହିଳାଙ୍କର (transgender women) ହରମୋନ ଥେରାପିର (hormone therapy) ଏହା ଉପାଦାନ ଥାଏ,[୧୫] ପ୍ରିଆପିଜ୍ମ (priapism) ପ୍ରତିଷେଧ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଦିଆଯାଏ,[୧୬] ଓ ବାଳକମାନଙ୍କର ସମୟ ପୂର୍ବ ଯୌବନ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି (early puberty) ରୋଗମାନଙ୍କ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଏହା ଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧୭] ଏହି ଔଷଧ ପାଟିରେ (by mouth) ଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧୧]
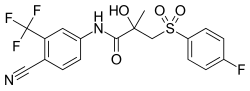 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Bicalutamide: /baɪkəˈluːtəmaɪd/ bye-kə-LOO-tə-myde[୨] Casodex: /ˈkeɪsoʊdɛks/ KAY-soh-deks[୩] |
| Trade names | Casodex, Cosudex, Calutide, Calumid, Kalumid, others |
| Synonyms | ICI-176,334; ZD-176,334 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697047 |
| data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth[୧] |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Well-absorbed; absolute bioavailability unknown[୬] |
| Protein binding | Racemate: 96.1%[୧] (R)-Isomer: 99.6%[୧] (Mainly to albumin)[୧] |
| Metabolism | Liver (extensively):[୪][୫] • Hydroxylation (CYP3A4) • Glucuronidation (UGT1A9) |
| Metabolites | • Bicalutamide glucuronide • Hydroxybicalutamide • Hydroxybicalutamide gluc. (All inactive)[୪][୧][୭][୮] |
| Elimination half-life | Acute: 5.8 days[୯] Chronic: 7–10 days[୧୦] |
| Excretion | Feces: 43%[୪] Urine: 34%[୪] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.100 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H14F4N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 430.373 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture (of (R)- and (S)-enantiomers) |
| Melting point | 191 to 193 °C (376 to 379 °F) (experimental) |
| Boiling point | 650 °C (1,202 °F) (predicted) |
| Solubility in water | 0.005 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
ଏହାର ପାର୍ଶ୍ୱ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟାରେ ସ୍ତନ ବୃଦ୍ଧି (breast enlargement), ସ୍ତନ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା (breast tenderness) ଓ ଦେହ ଲାଲ ପଡ଼ିଯିବା (hot flashes) ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।[୧୧] ପୁରୁଷମାନଙ୍କର ମହିଳାତ୍ୱ (feminization) ପ୍ରକାଶ ପାଏ ଓ ସେମାନେ ଯୌନ କ୍ରିୟାହୀନ (sexual dysfunction) ହୋଇଯାଆନ୍ତି ।[୧୮] ମହିଳାମାନଙ୍କର ଅଳ୍ପ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଏହା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବାକୁ ଏଫଡିଏ (Food and Drug Administration ବା FDA) ମନା କରେ ।[୧୯][୧୧] ଗର୍ଭାବସ୍ଥାରେ ଶିଶୁର କ୍ଷତି ହୋଇପାରେ ।[୧୧] ପ୍ରାୟ ୧% ଲୋକଙ୍କର ବାଇକାଲୁଟାମାଇଡ ଯୋଗୁ ଟ୍ରାନ୍ସାଆମିନେଜ ସ୍ତର ବୃଦ୍ଧି (elevated liver enzyme) ପାଏ ।[୨୦][୨୧] ଏହା ଯୋଗୁ କ୍ୱଚିତ୍ ଯକୃତ୍ ବିଷକ୍ରିୟା (liver damage),[୧୧] ଓ ଫୁସଫୁସ ବିଷକ୍ରିୟା (lung toxicity) ଦେଖାଯାଇପାରେ ।[୬] ଯକୃତ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ଓ କ୍ଷତି ସଙ୍କଟ କମ୍ ଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଚିକିତ୍ସା ସମୟରେ ଲିଭର ଫଙ୍କସନ ଟେଷ୍ଟ (monitoring of liver enzyme) କରିବାକୁ ଉପଦେଶ ଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧୧]
ଆଧାର
ସମ୍ପାଦନା- ↑ ୧.୦ ୧.୧ ୧.୨ ୧.୩ ୧.୪ Cockshott ID (2004). "Bicalutamide: clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 43 (13): 855–878. doi:10.2165/00003088-200443130-00003. PMID 15509184.
These data indicate that direct glucuronidation is the main metabolic pathway for the rapidly cleared (S)-bicalutamide, whereas hydroxylation followed by glucuronidation is a major metabolic pathway for the slowly cleared (R)-bicalutamide.
- ↑ Finkel, Richard; Clark, Michelle Alexia; Cubeddu, Luigi X. (2009). Pharmacology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 481–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7155-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Sifton DW, PDR Staff (2002). PDR Drug Guide for Mental Health Professionals. Thomson/PDR. ISBN 978-1-56363-457-4.
- ↑ ୪.୦ ୪.୧ ୪.୨ ୪.୩ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;LemkeWilliams2008ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;GrosseCampeau2013ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ ୬.୦ ୬.୧ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;Dart2004ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ Dole EJ, Holdsworth MT (1997). "Nilutamide: an antiandrogen for the treatment of prostate cancer". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 31 (1): 65–75. doi:10.1177/106002809703100112. PMID 8997470.
page 67: Currently, information is not available regarding the activity of the major urinary metabolites of bicalutamide, bicalutamide glucuronide, and hydroxybicalutamide glucumnide.
- ↑ Schellhammer PF (September 2002). "An evaluation of bicalutamide in the treatment of prostate cancer". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 3 (9): 1313–28. doi:10.1517/14656566.3.9.1313. PMID 12186624.
The clearance of bicalutamide occurs pre- dominantly by hepatic metabolism and glucuronidation, with excretion of the resulting inactive metabolites in the urine and faces.
- ↑ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;Skidmore-Roth2013ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;JordanFurr2010ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ ୧୧.୦ ୧୧.୧ ୧୧.୨ ୧୧.୩ ୧୧.୪ ୧୧.୫ ୧୧.୬ ୧୧.୭ "Bicalutamide". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ↑ Wass, John A.H.; Stewart, Paul M. (28 July 2011). Oxford Textbook of Endocrinology and Diabetes. OUP Oxford. pp. 1625–. ISBN 978-0-19-923529-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Shergill, Iqbal; Arya, Manit; Grange, Philippe R.; Mundy, A. R. (2010). Medical Therapy in Urology (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 40. ISBN 9781848827042.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Williams, Hywel; Bigby, Michael; Diepgen, Thomas; Herxheimer, Andrew; Naldi, Luigi; Rzany, Berthold (22 January 2009). Evidence-Based Dermatology. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 529–. ISBN 978-1-4443-0017-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Gooren, LJ (31 March 2011). "Clinical practice. Care of transsexual persons". The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (13): 1251–7. doi:10.1056/nejmcp1008161. PMID 21449788.
- ↑ Yuan J, Desouza R, Westney OL, Wang R (2008). "Insights of priapism mechanism and rationale treatment for recurrent priapism". Asian Journal of Andrology. 10 (1): 88–101. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00314.x. PMID 18087648.
- ↑ Jameson, J. Larry; De Groot, Leslie J. (25 February 2015). Edndocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2425–2426, 2139. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Elliott S, Latini DM, Walker LM, Wassersug R, Robinson JW (2010). "Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer: recommendations to improve patient and partner quality of life". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 7 (9): 2996–3010. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01902.x. PMID 20626600.
- ↑ Shapiro, Jerry (12 November 2012). Hair Disorders: Current Concepts in Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management, An Issue of Dermatologic Clinics. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 187–. ISBN 1-4557-7169-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Casodex® (bicalutamide) Tablets" (PDF). FDA.
- ↑ Wellington K, Keam SJ (2006). "Bicalutamide 150mg: a review of its use in the treatment of locally advanced prostate cancer" (PDF). Drugs. 66 (6): 837–50. doi:10.2165/00003495-200666060-00007. PMID 16706554.