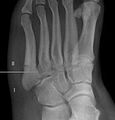
ଜୋନ୍ସ ଅସ୍ଥି ଭଗ୍ନ
ଜୋନ୍ସ ଅସ୍ଥି ଭଗ୍ନ (Jones fracture) ନାମ ଦିଆଯାଏ ଯେତେବେଳେ ପାଦରେ ଥିବା ପଞ୍ଚମ ମେଟାଟାର୍ସାଲ (fifth metatarsal) ଅସ୍ଥିର ଏପିଫିସିସ (base) ଓ ଡାଏଫିସିସ (middle part) ମଧ୍ୟବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ସ୍ଥାନ ଭାଙ୍ଗିଯାଏ ।[୭] ଏହି ଭଙ୍ଗା ଫଳରେ ପାଦର ମଧ୍ୟବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଓ ବାହାର ଦିଗରେ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ହୁଏ ।[୧] ବ୍ରୁଇସିଙ୍ଗ ଓ ଚାଲିବା ସମସ୍ୟା ମଧ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।[୨] ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଏହା ହଠାତ୍ ହୁଏ ।[୩]
| ଜୋନ୍ସ ଅସ୍ଥି ଭଗ୍ନ (Jones fracture) | |
|---|---|
| ପଞ୍ଚମ ମେଟାଟାର୍ସାଲ ଅସ୍ଥିର ପ୍ରକ୍ସିମାଲ ଡାଏଫିସିସ ଫ୍ରାକଚର | |
 ଏକ୍ସ-ରେ (Xray) ଚିତ୍ରରେ ଜୋନ୍ସ ଅସ୍ଥି ଭଗ୍ନ | |
| ବିଭାଗ | ଆଶୁ ଚିକିତ୍ସା ବିଭାଗ (Emergency medicine), ଅସ୍ଥିଶଲ୍ୟ ବିଭାଗ (orthopedics) |
| ଲକ୍ଷଣ | ମଧ୍ୟ ପାଦର ବାହାର ପାଖରେ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା, ବ୍ରୁଇସିଙ୍ଗ [୧][୨] |
| ଆକ୍ରାନ୍ତ ସମୟ | ହଠାତ୍[୩] |
| ଅବଧି | ସମ୍ପୁର୍ଣ୍ଣ ସୁସ୍ଥ ହେବାକୁ ୬-୧୨ ସପ୍ତାହ ଲାଗେ [୪] |
| କାରଣ | ପ୍ଲାଣ୍ଟ୍ରାର ଫ୍ଲେକ୍ସଡ (toes are pointed) ହୋଇଥିବା ପାଦ ଭିତର ଦିଗକୁ ମୋଡ଼ିହେଲେ [୫] |
| ରୋଗ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ ପଦ୍ଧତି | ଲକ୍ଷଣ ଅନୁଯାୟୀ, ଏକ୍ସ-ରେ (X-rays)[୨] |
| ସଠିକ ରୋଗ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ | ସୁଡୋ-ଜୋନ୍ସ ଅସ୍ଥି ଭଗ୍ନ (Pseudo-Jones fracture), ସାଧାରଣ ଗ୍ରୋଥ ପ୍ଲେଟ (normal growth plate)[୨][୬] |
| ଚିକିତ୍ସା | ପ୍ରଭାବିତ ପାଦରେ ଓଜନ ନ ନେବା, ପ୍ଲାସ୍ଟର (cast), ଅପରେଶନ[୪] |
ପାଦ ଫ୍ଲେକସନ ଫ୍ଲେକସନ (toes are pointed) ଓ ଆଡକସନ (bends inwards) ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ଥିବାବେଳେ ଏହି ଭଙ୍ଗା ହୁଏ ।[୫][୧] ନାଚ, ଟେନିସ ଖେଳ ବା ବାସ୍କେଟ ବଲ ଖେଳ ସମୟରେ ଭୂମିର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱରେ ଥିବା ପାଦର ହଠାତ ଦିଗ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହେବାରୁ ଏହିଭଳି ଭଙ୍ଗା ହୁଏ ।[୮][୯] ଲକ୍ଷଣ ଓ ଏକ୍ସ-ରେ (X-rays) ଚିତ୍ର ଦେଖି ରୋଗ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରାଯାଏ ।[୨]
ପ୍ରାରମ୍ଭରେ ଏହା ନିମନ୍ତେ ଗୋଟିଏ ପ୍ଲାଷ୍ଟର କ୍ୟାସ୍ଟ (cast) ଦିଆଯାଏ, ତାହା ଉପରେ ଓଜନ ନେବାକୁ ମନା କରାଯାଏ ଓ ଅତି କମରେ ୬ ସପ୍ତାହ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଏହାକୁ ରଖାଯାଏ ।[୪] ଏହି ଅବଧିରେ ଭଲ ନହୋଇଥିଲେ ଆରୁ ୬ ସପ୍ତାହ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ରଖାଯାଏ ।[୪] ଉକ୍ତ ଭଙ୍ଗା ସ୍ଥାନରେ ରକ୍ତ ସରବରାହ କମ ଥିବା ଯୋଗୁ ବେଳେବେଳ ଏହା ଭଲ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ଓ ଅପରେଶନ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହୁଏ । [୨] ଖେଳାଳୀମାନଙ୍କ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଓ ଭଙ୍ଗା ଅସ୍ଥି ଅଧିକ ବିସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ଅପରେଶନ ତୁରନ୍ତ କରିବାକୁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହୋଇପାରେ ।[୪][୭] ସନ ୧୯୦୨ରେ ରବର୍ଟ ଜୋନ୍ସ (Robert Jones) ନାମକ ଜଣେ ଅର୍ଥୋପେଡିକ ଚିକିତ୍ସକ (orthopedic surgeon) ନାଚ କଲାବେଳେ ଏହି ଭଙ୍ଗାରେ ପୀଡ଼ିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । [୧୦][୩]
-
ତିନି ଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ
-
୨ ଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ
ଆଧାର
ସମ୍ପାଦନା- ↑ ୧.୦ ୧.୧ ୧.୨ Eltorai, Adam E. M.; Eberson, Craig P.; Daniels, Alan H. (2017). Orthopedic Surgery Clerkship: A Quick Reference Guide for Senior Medical Students (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Springer. pp. 395–397. ISBN 9783319525679. Archived from the original on 2017-10-15.
- ↑ ୨.୦ ୨.୧ ୨.୨ ୨.୩ ୨.୪ ୨.୫ "Toe and Forefoot Fractures". OrthoInfo - AAOS. June 2016. Archived from the original on 16 October 2017. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ↑ ୩.୦ ୩.୧ ୩.୨ Valderrabano, Victor; Easley, Mark (2017). Foot and Ankle Sports Orthopaedics (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Springer. p. 430. ISBN 9783319157351. Archived from the original on 2017-10-15.
- ↑ ୪.୦ ୪.୧ ୪.୨ ୪.୩ ୪.୪ Bica, D; Sprouse, RA; Armen, J (1 February 2016). "Diagnosis and Management of Common Foot Fractures". American Family Physician. 93 (3): 183–91. PMID 26926612.
- ↑ ୫.୦ ୫.୧ Dähnert, Wolfgang (2011). Radiology Review Manual (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 96. ISBN 9781609139438. Archived from the original on 2017-10-15.
- ↑ Conaghan, Philip G.; O'Connor, Philip; Isenberg, David A. (2010). Musculoskeletal Imaging (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). OUP Oxford. p. 231. ISBN 9780191575273. Archived from the original on 2017-10-15.
- ↑ ୭.୦ ୭.୧ Joel A. DeLisa; Bruce M. Gans; Nicholas E. Walsh (2005). Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Principles and Practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 881–. ISBN 978-0-7817-4130-9. Archived from the original on 2017-01-07.
- ↑ Mattu, Amal; Chanmugam, Arjun S.; Swadron, Stuart P.; Tibbles, Carrie; Woolridge, Dale; Marcucci, Lisa (2012). Avoiding Common Errors in the Emergency Department (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 790. ISBN 9781451152852. Archived from the original on 2017-10-16.
- ↑ Lee, Edward (2017). Pediatric Radiology: Practical Imaging Evaluation of Infants and Children (in ଇଂରାଜୀ). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. Chapter 24. ISBN 9781496380272. Archived from the original on 2017-10-15.
- ↑ Jones, Robert (Jun 1902). "I. Fracture of the Base of the Fifth Metatarsal Bone by Indirect Violence". Ann Surg. 35 (6): 697–700. PMC 1425723. PMID 17861128.
ବାହ୍ୟ ଲିଙ୍କ
ସମ୍ପାଦନା| ଶ୍ରେଣୀବିଭାଗ | |
|---|---|
| ବାହାର ଉତ୍ସ |
- Jones fracture - wheelessonline.com